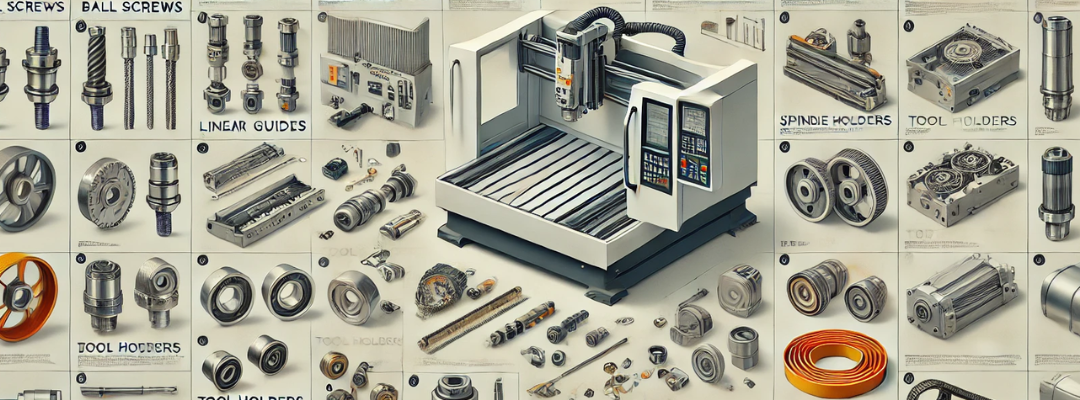
A CNC machine consists of numerous parts that work together to perform precise machining operations. Below is a general list of key spare parts commonly used in CNC machines:
1. Mechanical Components
- Ball Screws: Convert rotational motion into linear motion with high precision.
- Linear Guideways: Provide smooth linear motion for the machine’s axes.
- Bearings: Support rotating parts like spindles and ball screws.
- Couplings: Connect motors to ball screws or other machine elements.
- Tool Holders (e.g., BT, HSK, CAT): Hold cutting tools in place on the machine’s spindle.
- Collets: Grip the tool in the spindle or tool holder.
- Spindle Bearings: Ensure smooth rotation of the spindle.
2. Electrical Components
- Servo Motors: Drive the machine’s axes with precise motion control.
- Stepper Motors: Control the incremental movement of the machine.
- Spindle Motor: Powers the spindle, enabling the cutting tool to rotate.
- Encoders: Provide feedback on the position of moving parts.
- Limit Switches: Detect the limit of motion to prevent overtravel of machine axes.
- Proximity Sensors: Detect the position of machine parts or tools.
- Power Supply Units: Provide power to various machine components.
- Cables and Connectors: Connect various electrical components for power and signal transmission.
3. Hydraulic/Pneumatic Components
- Hydraulic Pumps: Control the movement of heavy parts in some CNC machines.
- Solenoid Valves: Control the flow of air or fluid in hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
- Pneumatic Cylinders: Provide movement for components such as tool changers.
4. Control System Components
- CNC Controller Unit: The brain of the CNC machine, controlling all operations and processing G-code.
- Control Panel: Where operators input commands and control the machine manually.
- Display Monitor: Shows machine parameters, operating status, and CNC program details.
- Keypads or Touchscreen Interfaces: For operator input to control the machine functions.
5. Cooling and Lubrication Components
- Coolant Pumps: Supply cutting fluid to the tool and workpiece for cooling.
- Lubrication Pumps: Deliver oil or grease to moving parts for smooth operation.
- Coolant Nozzles: Direct coolant flow to the cutting zone.
6. Tooling and Workholding Components
- Vices and Clamps: Hold the workpiece securely in place.
- Chucks: Attach to the spindle to hold larger or specific types of tools.
- Fixture Plates: Custom plates designed to hold workpieces in place during machining.
- Tool Turrets (for lathes): Hold multiple tools and rotate them into position as needed.
7. Miscellaneous Components
- Tool Probes: Measure tool length and diameter for precise tool positioning.
- Workpiece Probes: Measure the workpiece position and alignment on the machine table.
- Filters (Coolant and Air): Keep the coolant and machine’s air systems clean.
- Fan Units: Cool down the machine components like the control unit or motors.
- Belts: Transmit power from the motors to other moving parts.
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Protect the machine’s electrical system from overloads.
Having these spare parts on hand can help minimize downtime and ensure the CNC machine operates efficiently and with precision.

Recent Comments